
-Luther Burbank
In the lush tapestry of horticulture, the art of propagation and breeding serves as the foundation for the growth and diversification of plant life. This intricate process involves the reproduction and development of new plant specimens, unlocking a world of possibilities for avid gardeners and horticulturists. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the realms of propagation and breeding, exploring the methods, significance, and the magic that unfolds behind the scenes.
Propagation, at its core, is the art of creating new plants from existing ones, a process that not only sustains genetic traits but also preserves rare species and fosters sustainable growth. The choice of propagation method depends on various factors, including the type of plant and the desired outcome. Matching the method to the characteristics of the plant ensures optimal success.
Let us delve into the various ways in which propagation can be improved:
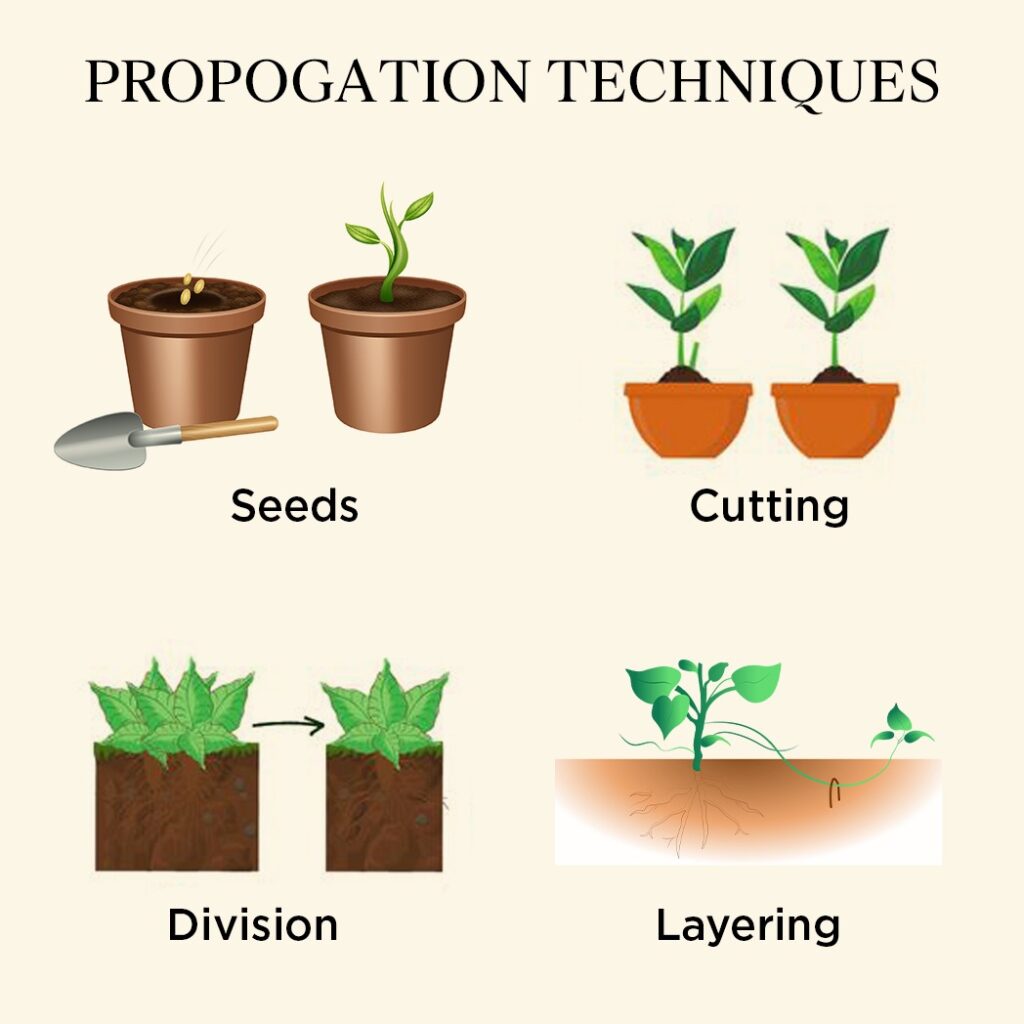
Seeds: The Natural Miracle
Seeds, the tiny marvels of nature, encapsulate the potential for new life. Understanding the life cycle of plants through seeds is key to unlocking the full spectrum of propagation possibilities.
Cuttings: Harnessing the Power of a Snippet
Cuttings involve taking a portion of a parent plant and encouraging it to develop roots. This method allows for the cloning of plants with desirable traits, providing a shortcut to replicating excellence.
Division: Splitting for Prosperity
Division is a method where established plants are divided into sections, each capable of growing independently. This is particularly effective for plants with multiple stems or bulbs.
Layering: Encouraging Self-Renewal
Layering involves inducing a branch or stem to produce roots while still attached to the parent plant. Once roots are established, the new plant can be separated and transplanted.
Breeding
Breeding in horticulture is a deliberate and meticulous process which involves the intentional manipulation and combination of genetic material to enhance desirable characteristics or create entirely new varieties. As we explore the nuances of breeding in horticulture, we unveil the secrets behind the mesmerising diversity and resilience that characterise the plant kingdom. Breeding is an effort to elevate specific traits or introduce entirely new varieties. The process involves meticulous selection and controlled pollination techniques:
Selective Breeding: Identifying Desirable Traits

Selective breeding focuses on identifying and intensifying desirable traits, such as vibrant colours, disease resistance, or unique growth patterns. This method relies on careful observation and controlled cross-breeding.
Hybridization: Crossing for Unique Outcomes
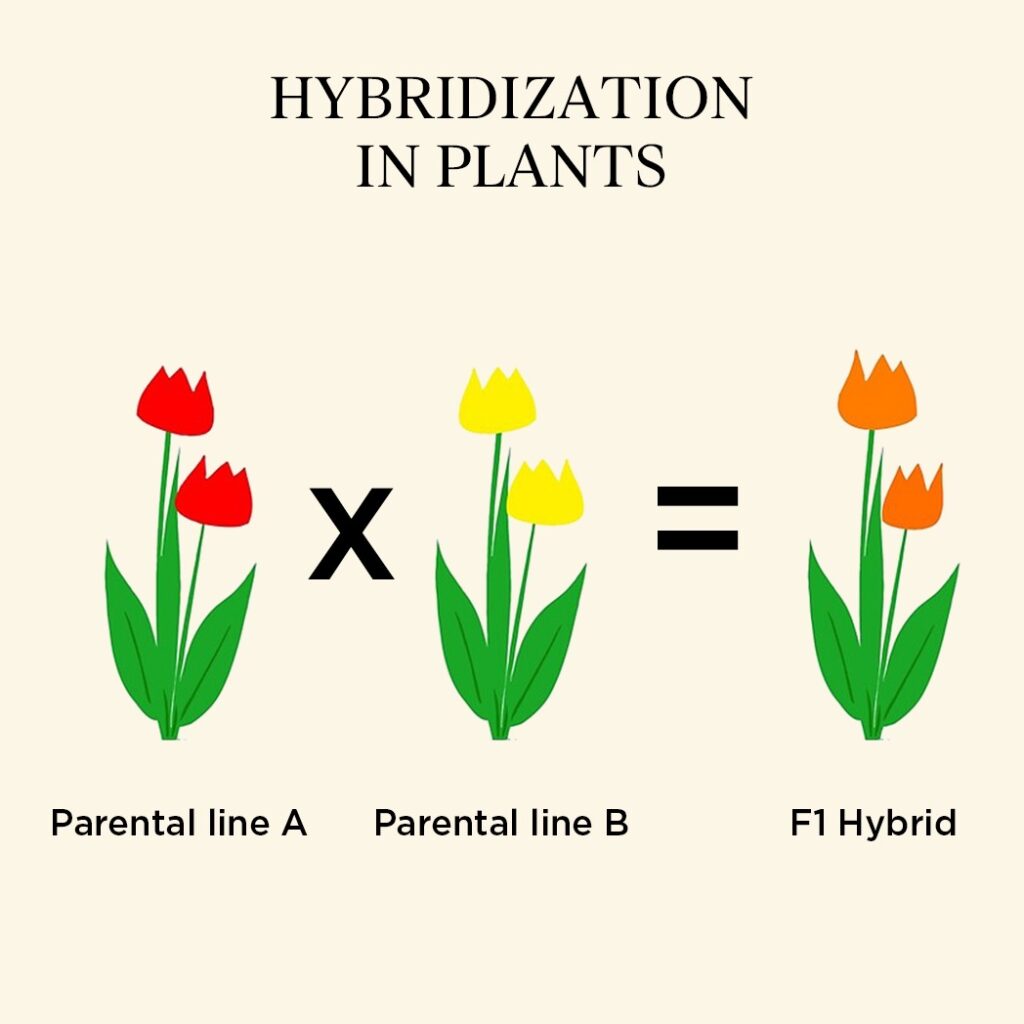
Hybridization involves crossing different species to produce plants with a combination of desirable traits from each parent. This method allows for the creation of entirely new varieties with unique characteristics.
Challenges and Solutions: Navigating the Genetic Landscape
As we embark on this journey, challenges arise, including the importance of maintaining genetic diversity and ethical considerations related to breeding practices:
- Genetic Diversity: Preserving Nature’s Blueprint – Maintaining a diverse gene pool is crucial to the long-term health and sustainability of plant populations. Strategies to counter inbreeding ensure that genetic diversity is preserved.
Ethical Considerations: Balancing Innovation and Responsibility – Striking a balance between innovation and ecological responsibility is paramount. Addressing concerns related to genetically modified organisms (GMOs) ensures that advancements in horticulture align with ethical standards.
In the tapestry of horticulture, propagation and breeding emerge as the threads weaving a story of growth, innovation, and conservation. Armed with the knowledge shared in this comprehensive guide, horticulturists embark on a journey of cultivating life, contributing to the ever-evolving landscape of plants and flowers that enrich our world.




