The main function of stem is grow and bear leaves, flowers fruits and branches. In short branches help plant spread.
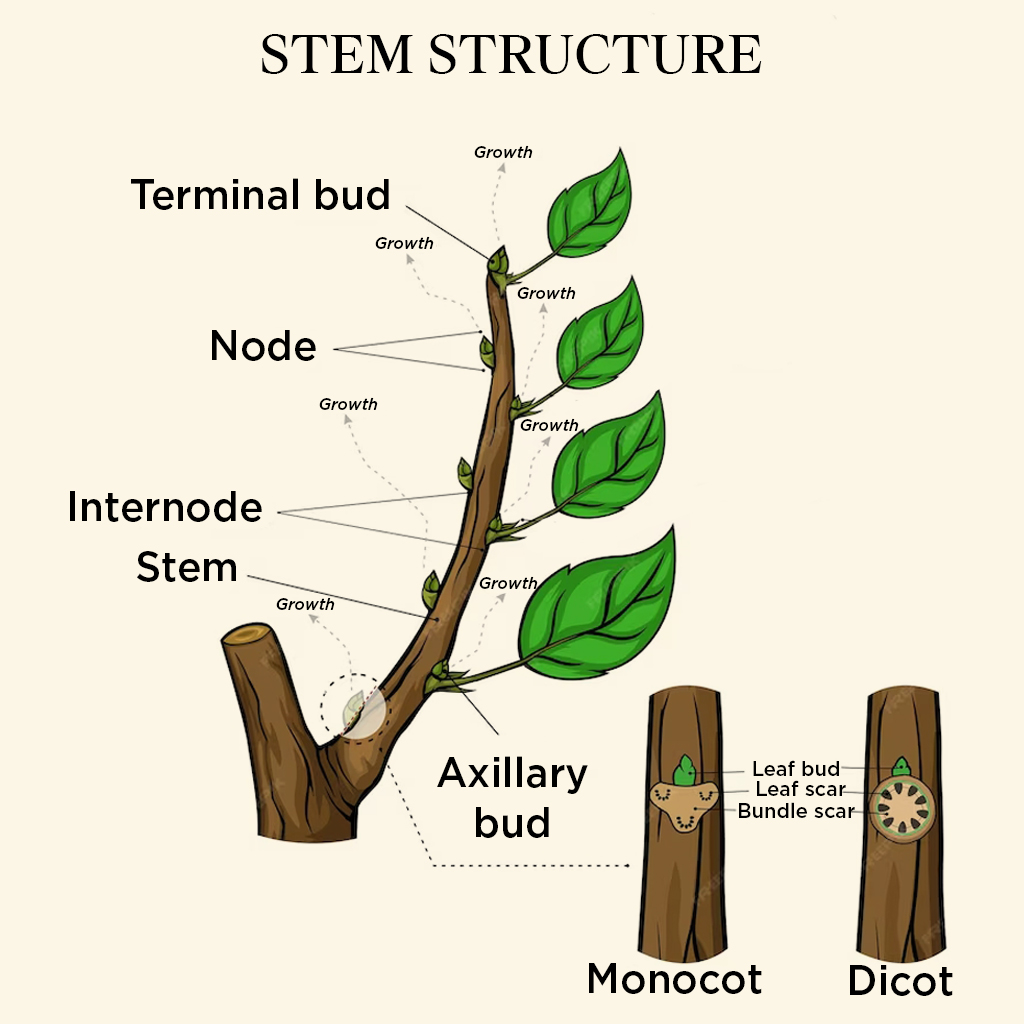
Nodes and Internodes
The stem is the ascending part of the axis bearing branches, leaves, flowers and fruits. It develops from the plume of the embryo of a germinating seed.
The stem bears nodes and internodes. The regions of the stem where leaves are born are called nodes while internodes are the portions between two nodes.
ADAPTATIONS OF STEM : In continuation to magical way of nature, stems sometimes take a non-conventional shape, size or colour than regular straight green/brown line. Lets look at such adaptations
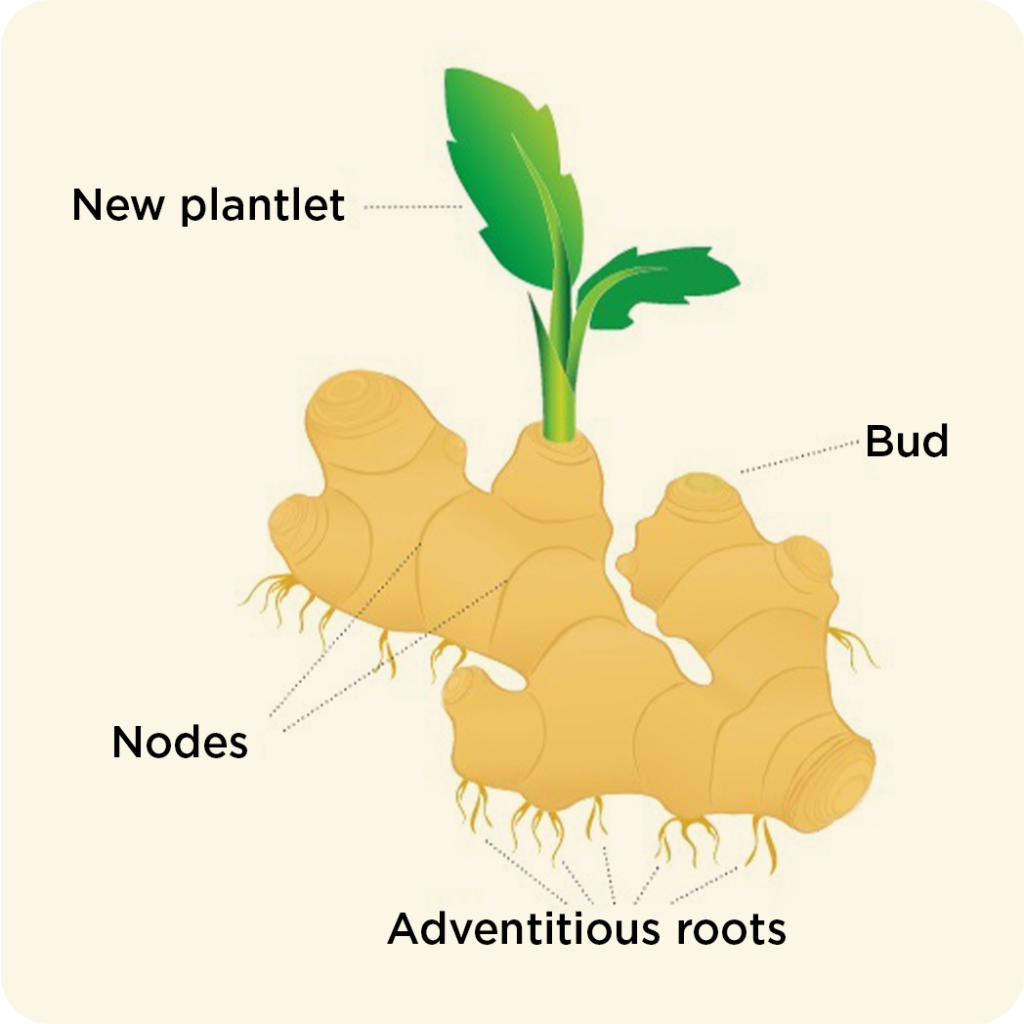
Rhizomes
Rhizomes are fattened swollen stems which used extra space (swollen) to store starch and nutrients for unfavourable days. Rhizomes are non-green with clearly visible nodes and internodes. Common examples of rhizomes are ginger and snake plant.
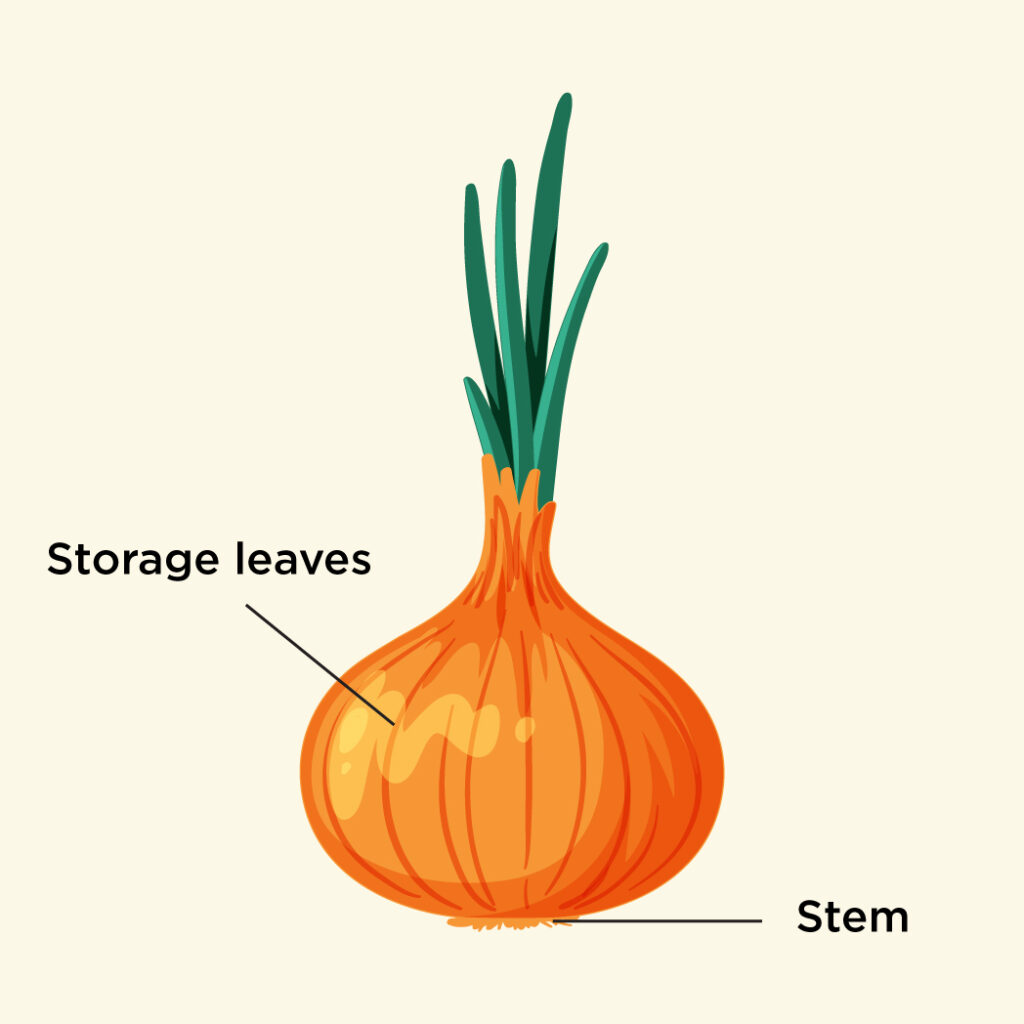
Bulb
The bulb is fleshy multi-layered stem which again stores nutrients and water for unfavourable conditions called A sheath of dry membranous scale leaves protected the tunicate bulb. For example: onion and lilies.
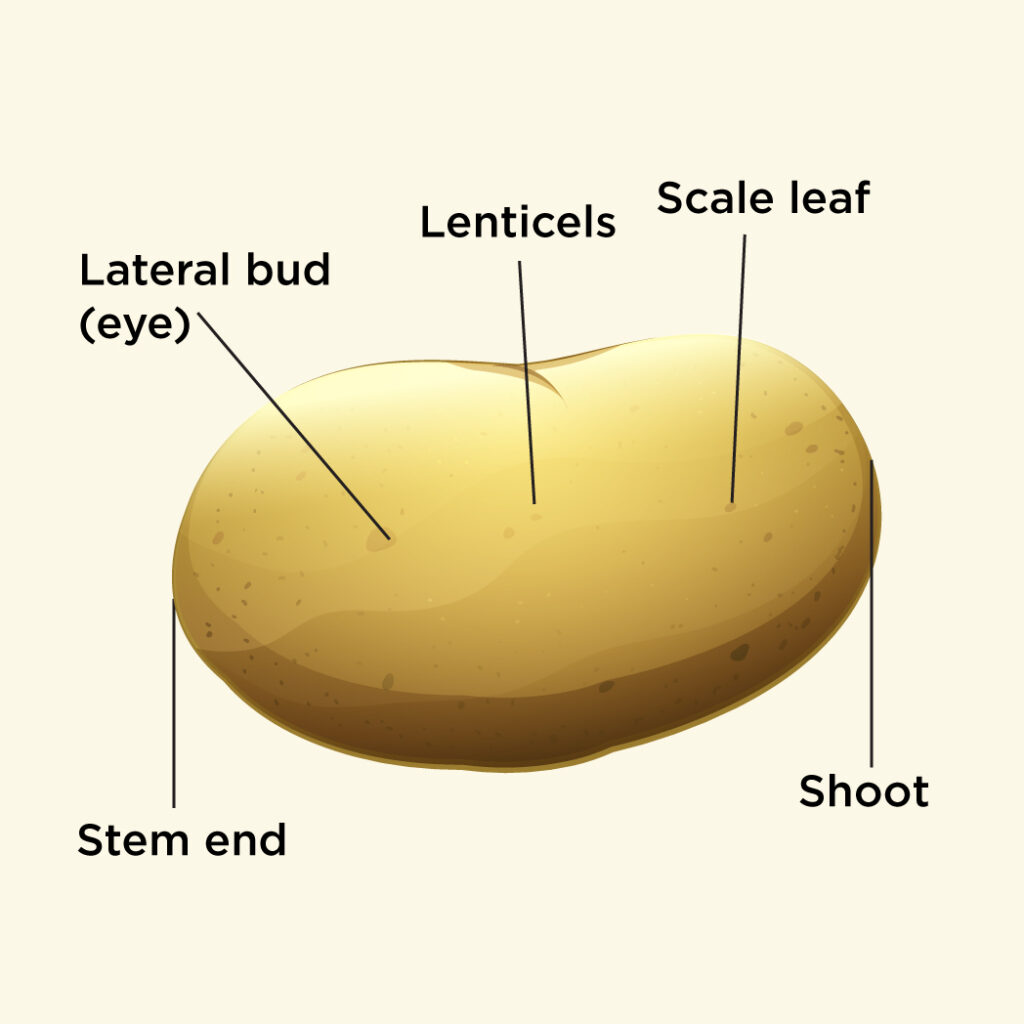
Tuber
The tuber is a fleshy part of the plant which stores food. For Example: Potato
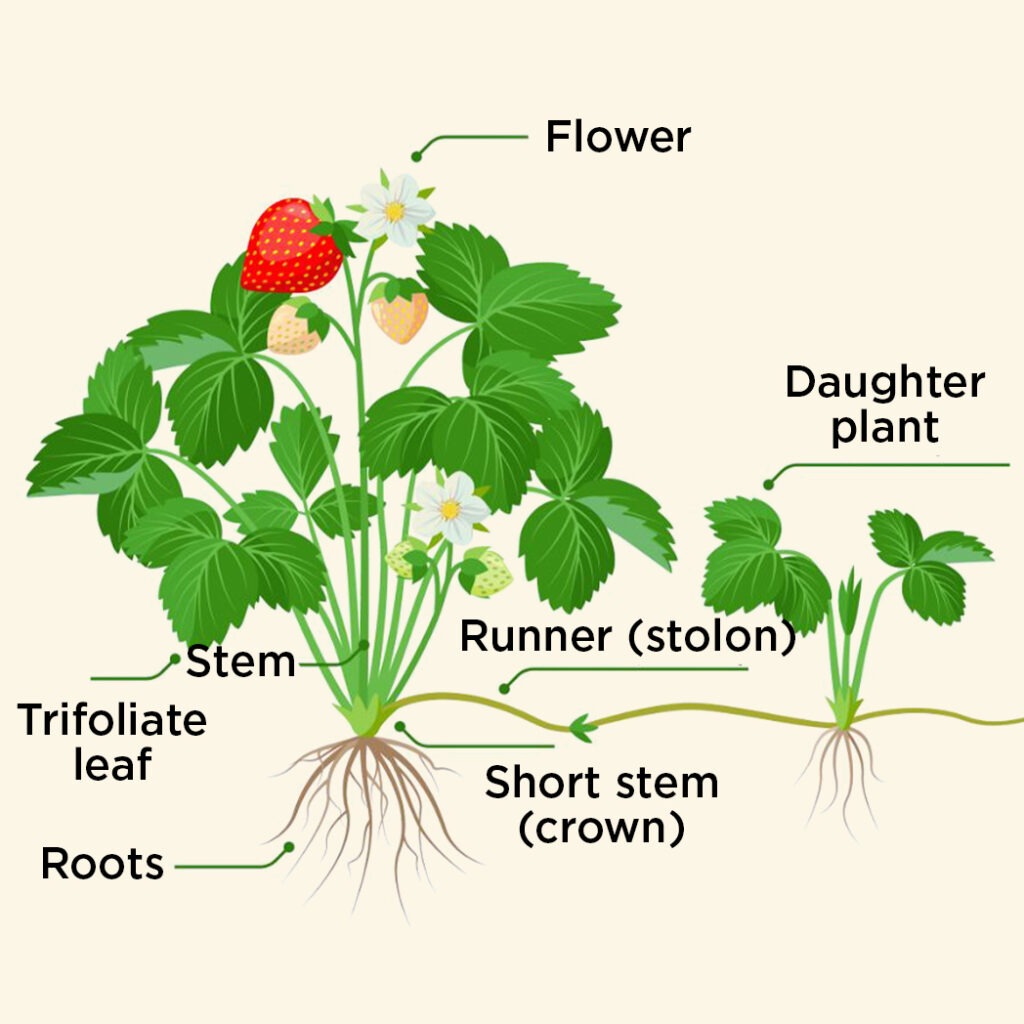
Stolon
Stolon are stems that start from soil surface grow aerially and later bend towards ground to propagate new growth. For this particular growing style they are also called runners. Eg: Jasmine, mint
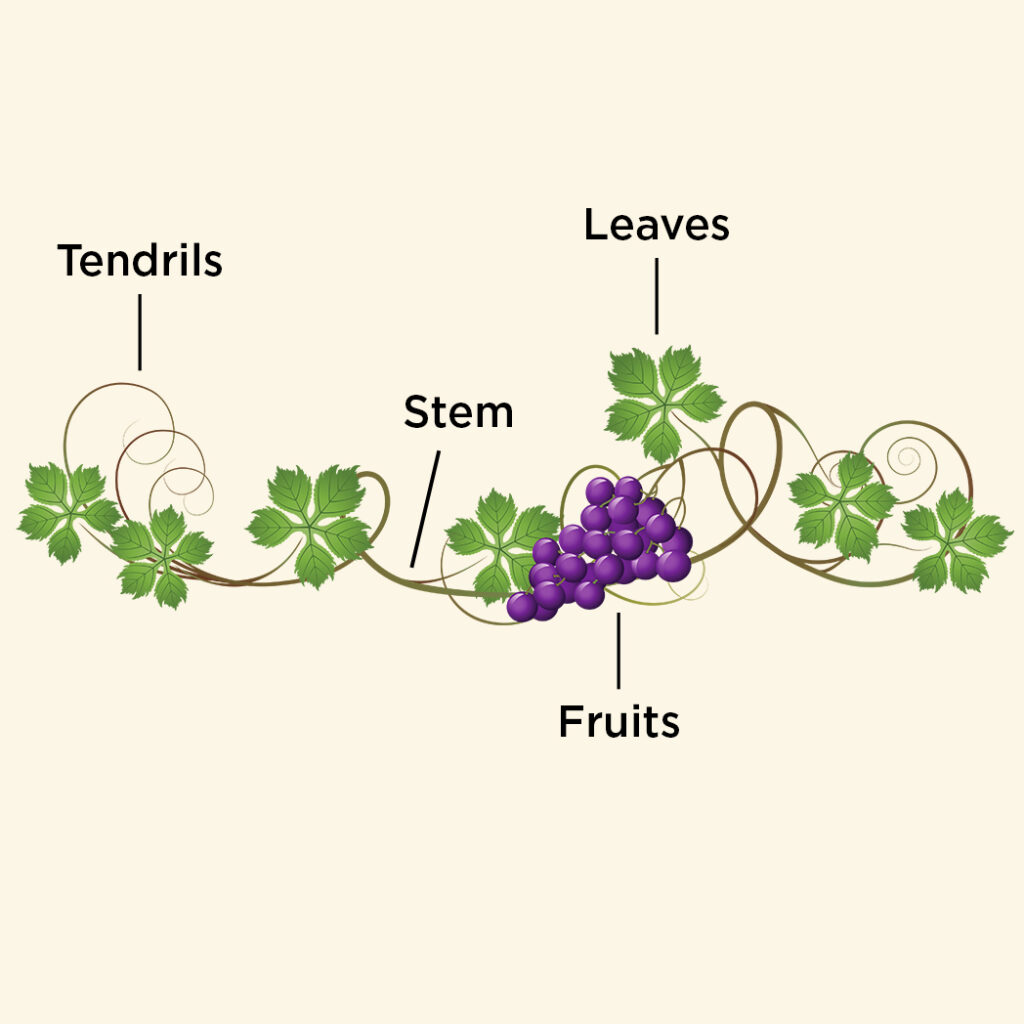
Climber
Stem adapting itself to claiming purpose, climber stems modify itself to leafless thread like shape know as tendrils. Shape of tendrils is optimized of latching on to any surface and grow vertically “climbers.. E.g. cucumber, pumpkin, grapes etc.