
Light is crucial factor governing growth of plant at every stage. Plant create their own food (Carbohydrate) using light carbon dioxide and water, this process is know as “photosynthesis”. Remember this is same carbohydrate or carb that we humans need to meet of energy requirement of our body. So to Plants light is essential for creating food, all plants need to make their food in order to survive and grow. Hence you sometimes hear no plant is Indoor plant completely, what it means is they need some bit of light may be not direct, but indirect diffused or low intensity depending on plants.
Function of Light in Plant Growth
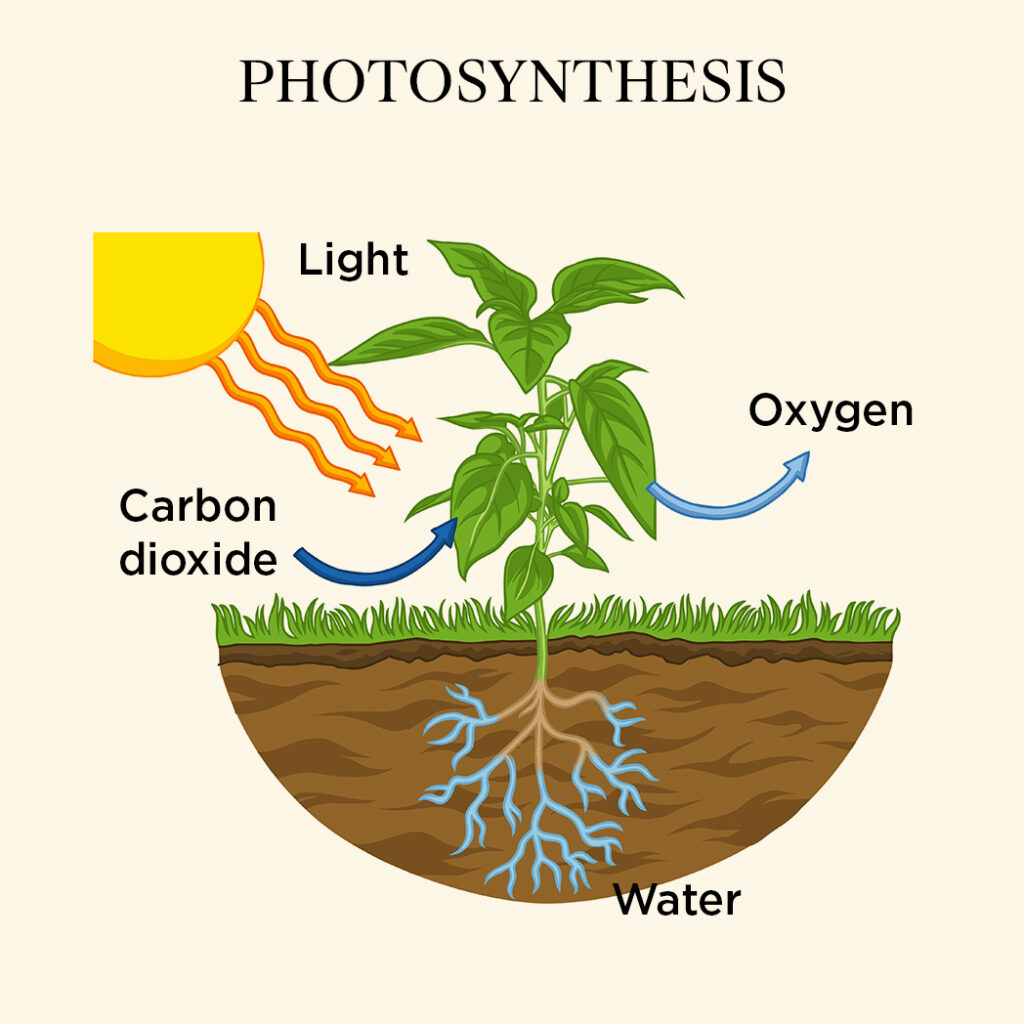
Let us understand photosynthesis in detail once again, Now plants are autotroph – a organism which can create their food within their body and don’t rely on others for food like us humans.
We learnt in earlier chapters that plant leaves have tiny organ called chloroplast and chloroplast has a pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll uses light to convert water and carbon dioxide to create cellulose also known as sugar or carbohydrate (plant food). Chemically process looks as below –
Why Plants are our Friend?
Take a closer look at the chemical equation of photosynthesis process takes away carbod dioxide (CO2) and produces same amount of oxygen (O2) we humans do reverse- inhale this oxygen and exhale CO2. This shows how important plants are for our own life and without them we cannot live.

Importance of Light Spectrum
Sun light is combination of 7 (rainbow) colors, remember the rainbow or prism breaks the light in into 7 different bands called V-iolet I-ndigo B-lue G-reen Y-ellow O-range R-ed.
These colors represent 7 different wavelength bands which combined together makes visible part of light.
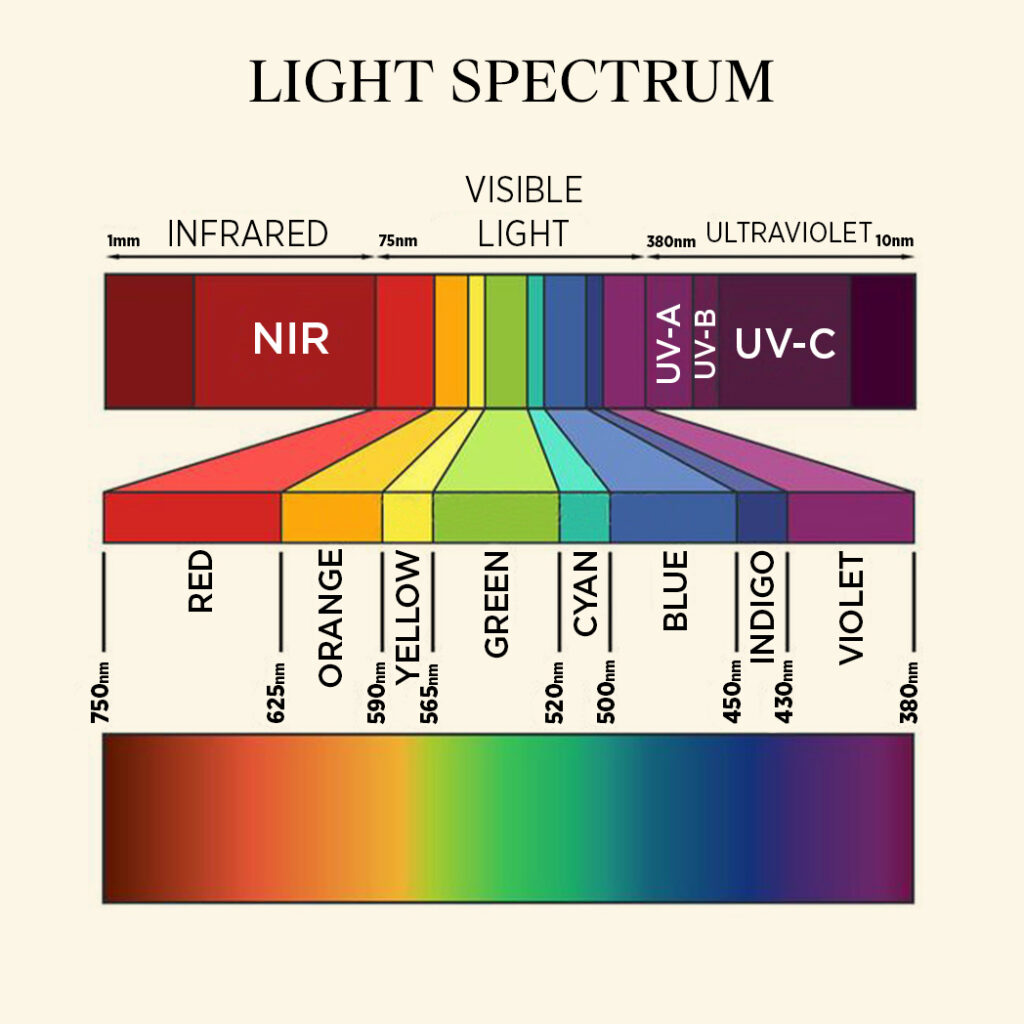
Chlorophyll in the leaves uses only red and blue part of light during photosynthesis and reflects green light. Which is why chlorophyll looks green to our human eye.
These wavelengths have different impacts:
Blue Light – This light has high energy and affects the leaf growth (also called vegetative growth) of plants. Blue light has an impact on chlorophyll production, but you only need it very small quantities when compared to red light. Plants that do not get adequate blue light start getting weaker, with yellow streaks in the leaves instead of green.
Red Light– Red light is important for flowering and fruiting in the plants. Plants that do not get adequate Red show delay in flowering or very weak blooming stage in plants.
Light Duration/Exposure
Intensity of the light for an indoor plant depends on how distance from source of light – open balcony or terrace to window sills to few feet away from window intensity keeps on changing.
4 Ds
Now lets understand 4Ds that governs light available in a particular spot in your in modern day house
- Directions: If you have East or south east facing houses and balcony you get the mild morning sun light which considered ideal, a North West or west facing balcony get maximum hours of sunlight but includes harsh afternoon sun light and heat.
- Deflection/Obstruction/Shade: In modern day apartment light also depends on building and trees around our house, shades and curtains etc. that may be blocking sun light partially or fully. e.g a tall building in front of my west facing balcony may limit or diffuse the otherwise harsh afternoon sun says and protect my plants.
- Distance: Intensity of the light for a home plant depends on distance from source of light. As you walk from open balcony to window sills living room or few steps towards the hallway from window the intensity will changing rapidly.
- Duration (Hours) of Sun Light: In some cases the duration of light available to plant also is factor in growth of plants . Flowering plant generally need longer hours of sun for flowering. Kalanchoes for examples flowers only when days are 7-10 hrs. At the same time almost all plants requires few minimum 8+ hours per day of darkness to develop and grow.
How to Ace Light In Gardening?
Now that we have science of light working behind plant growth. Let’s try understand few simple hacks to get it right. In order to get the right light for our plant we must know “Light Available” in our house depending direction, deflection, distance and duration.
Take a look around your house, make a note of how much light each section of house get where we can put plant(s).
Divide the area in direct sun light, bright sun light, medium light and low light. We refer low light areas as the part of your house where you will need artificial light in order to reed and write with straining your eyes.
You can see sun rays falling either morning/evening. To make it simple we are giving you 3 easy way to categorize light in your house
Duration : Simple observation of pattern and duration of sun rays falling in your area thought the day.
Task : Ability to read or thread a needle in certain area without artificial lights.
Light Meter: There are millions of light meter phone app to give you reading of light available in your house. Remember to switch off any artificial light when taking measurement.
Science of light measurement is quite evolved to simplify let understand there are two popular way to measure light. As we know already light is made of combination 7 color light plant only require Red and Blue spectrum of light and reflect green band while humans mostly depend and relate with green brand and that’s why our common home artificial lights are heavy on green band and have very little to offer to plant (red and blue).
Let see how the measurement differ in keeping this in mind
Human’s PoV: Lux or Foot candle is used to measure light as perceived by humans. This measurement is suitable more for architectural or photography use when end consumer of light is human.
Plant’s PoV: PAR or PPFD is measure of light as perceived by plants. This measurement focuses on red and blue spectrum which is useful for photosynthesis in plants.
For our home gardening purpose using Lux meter or PPFD meter apps will not make much of difference but it is good to know for from knowledge point of view.
Class
Direct
Bright Light
Indirect/Medium
Low Light
Duration
5+ Hrs Sun
1-2 hr of Partial Sun
Rays fall few feet away from spot most of the day or area or protected via shade/curtain.
No direct Ray
Location Specifics
terrace/balcony /open area
east or west facing window area with either morning or sun set rays falling.
No direct sun rays but enough light to read or write
No direct sun rays one would ideally need bulbs or lamps to for task like reading book, needle thread
Light Intensity
Lux 2000+
Lux 1000-2000
Lux 500-1000
Lux <500
Once you have categorized light in your house it very simple to find plants suitable to these condition
How plants are affected by too little or too much light?
-
- Plants turning pale green to yellow to white.
- Plant stems become long and thin in order be search and find source of light.
- In lack of adequate light you will notice spaces on stems between the leaf nodes making it appear less bushy/fuller. Or may start dropping leaves
- In flowering plant flowering will stop, in variegated variety (leaves that are white and green) you will notice loss of variegation in leaves with solid green.
According to the availability of light plants are grouped into three types which are as follows:
2. Medium Light Plants
3. High Light Plants

Low Light(PPF: 50-150 or Lux<500)
A low-light plant would be suitable for a north window or a fairly dark corner. Low-light plants require little to no direct light. In environments with less light, plants grow more slowly and use less water.
While a plant may tolerate lower light growing conditions, more light may be required to promote dense foliage and flowering.
Medium Light(PPF: 150-250 Lux 500-100)
A medium-light plant would be suitable for east-facing windows or located near a west-facing window, but out of direct light. You would need artificial lighting for starting seeds in medium light.
Like the low light plants, these plants will not dry out as quickly. Avoid overwatering by feeling the soil.
High Light(PPF: 250-450 umol m-2s-1 / more than 20 watts)
A high-light plant would be suitable for brightly lit locations such as south- or southwest-facing windows. You may be able to start seeds without artificial lighting, but seeds that need more time indoors, such as tomatoes and peppers, may become leggy without extra light.
High-light areas can be warm, making plants dry out faster. Check these plants more frequently and water when soil is dry.
(PPF-Photosynthetic Photon Flux, it measures the photo synthetically active photons emitted by lighting system per second)




