What is root? Root provides anchoring or support to plants to stand on ground, collects useful minerals and water from soil, enables PGR – plant growth regulators and works as storage for plant food
‘We believe that there is no structure in plants more wonderful, as far as its functions are concerned, than the tip of the radicle’ – Darwin and Darwin (1880).
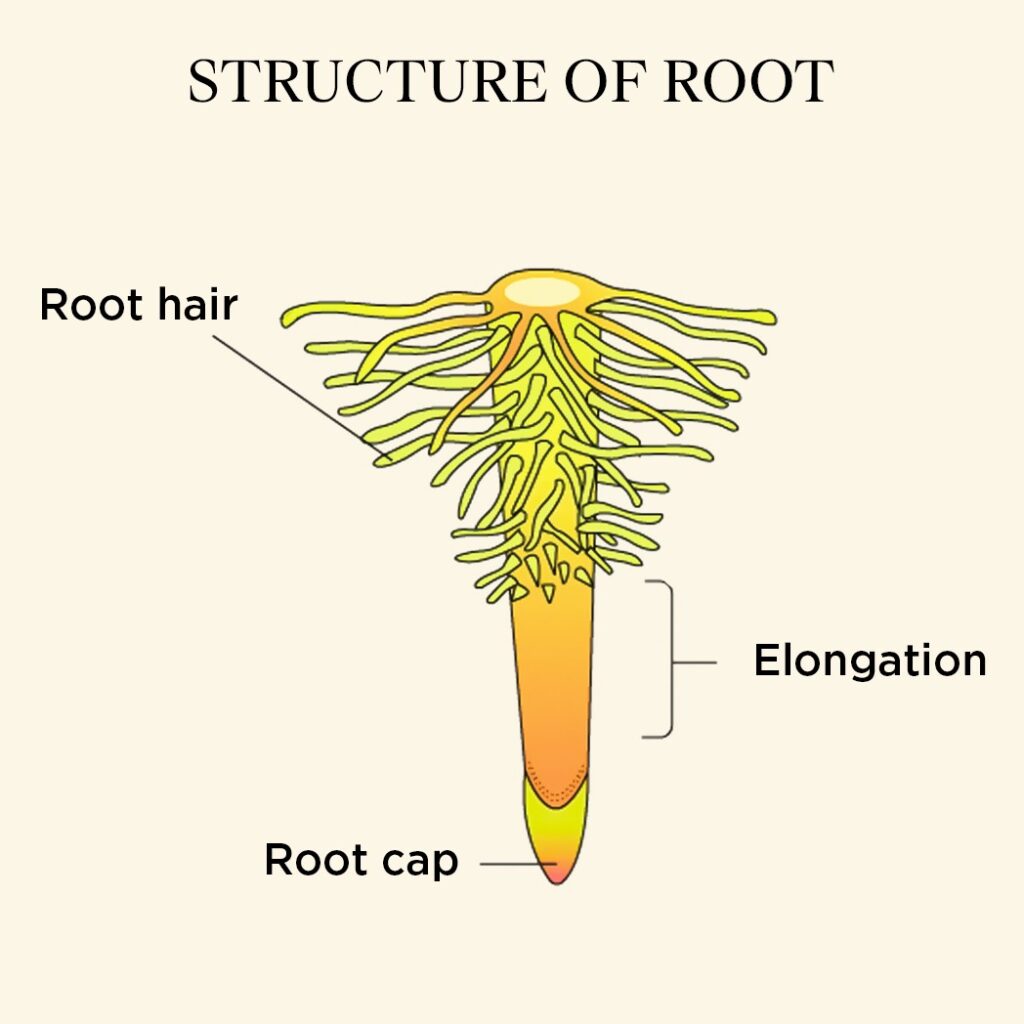
Parts of Root
Root Cap is relatively harder tissue present at the tip of the roots. They protect softer part of the roots from environmental stress. They also work as sensor reading and sending information about environmental conditions. By design root caps are made in such way that they can sense the gravitational force and ensure roots grow in downward direction.
Area protected behind root cap is filled with cells and tissues whose primary job is to grow and elongate to increase size of the root. If the root grow longer they get access to more water and nutrients in soil and thus a healthier plant.
The parts above the region above the root cap is the region of elongation where cells undergo elongation and enlargement to increase the length of the root.
Root Hairs is the side lateral extension of roots, their primary function is to collect water and nutrient from soil and carry them to desired destination within plant system.
ADAPTATION OF ROOTS : However, the roots are magical in terms of taking special role for the survival of plant in certain situations.
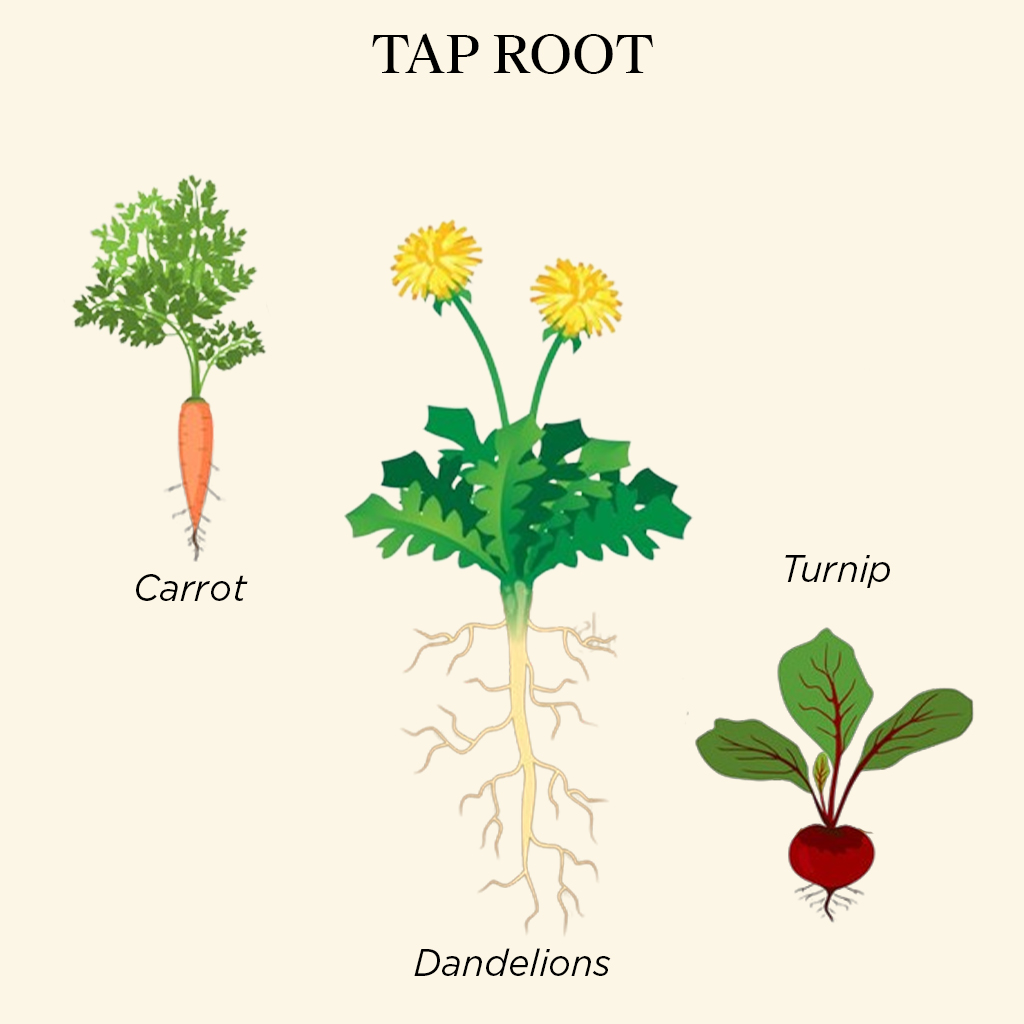
Tap Root
Example – Dandelion, Turnip, and Carrots
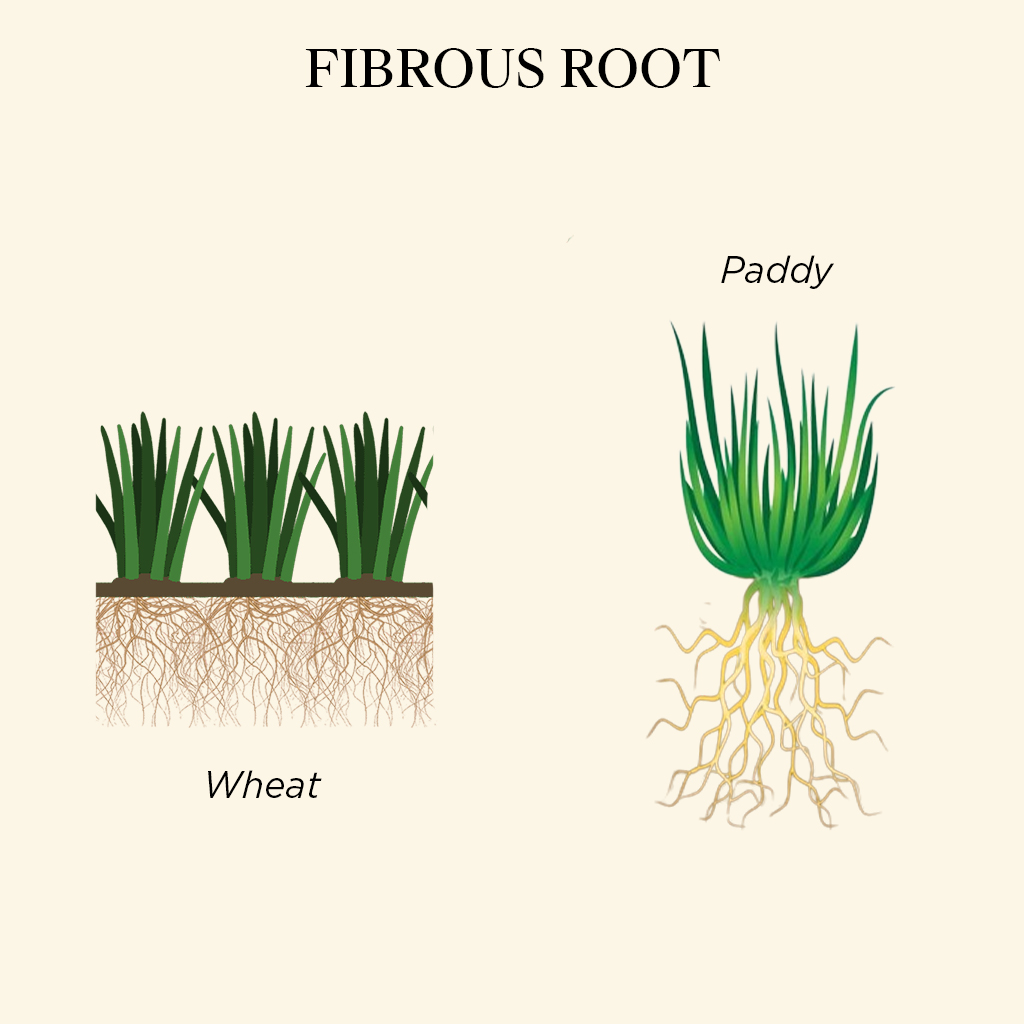
Fibrous Root
Example – Wheat, Paddy
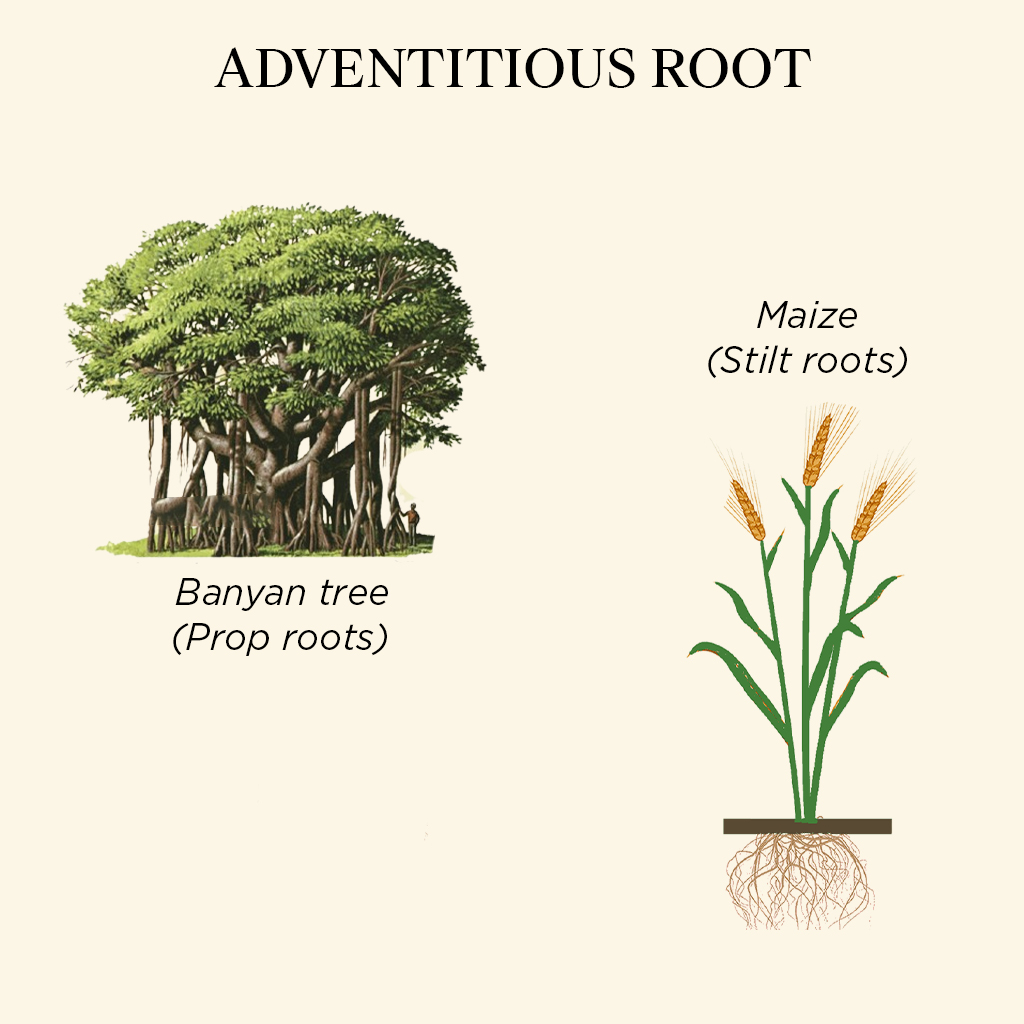
Adventitious Root
Example – Banyan Tree (Prop Roots), Maize (stilt roots).