
Let’s start to understand “soil” a widely used term in the world of gardening. I personally feel soil is where the most unseen magic of gardening happens and we will as progress in this chapter. So what is Soil? From the science stand point Soil is combination of different earth materials which go through a complex sequence of event for millions of years. Yes !! the soil in our garden, which an unaware person may casually refers as “dirt” or “dust”, takes these many years to form soil. The complicated reactions and simple rearrangement of matter namely- Humification, Eluviation, Illuviation over years makes this “dust” real “Gold”.
The term soil is derived from Latin word “Solum” which means the floor. Our India Vedic literatures from early 5000BC, gives at most respect to soil (or land)– As the “Mother” – supporting and nourishing all life on earth.
-Dokuchaiev father of soil science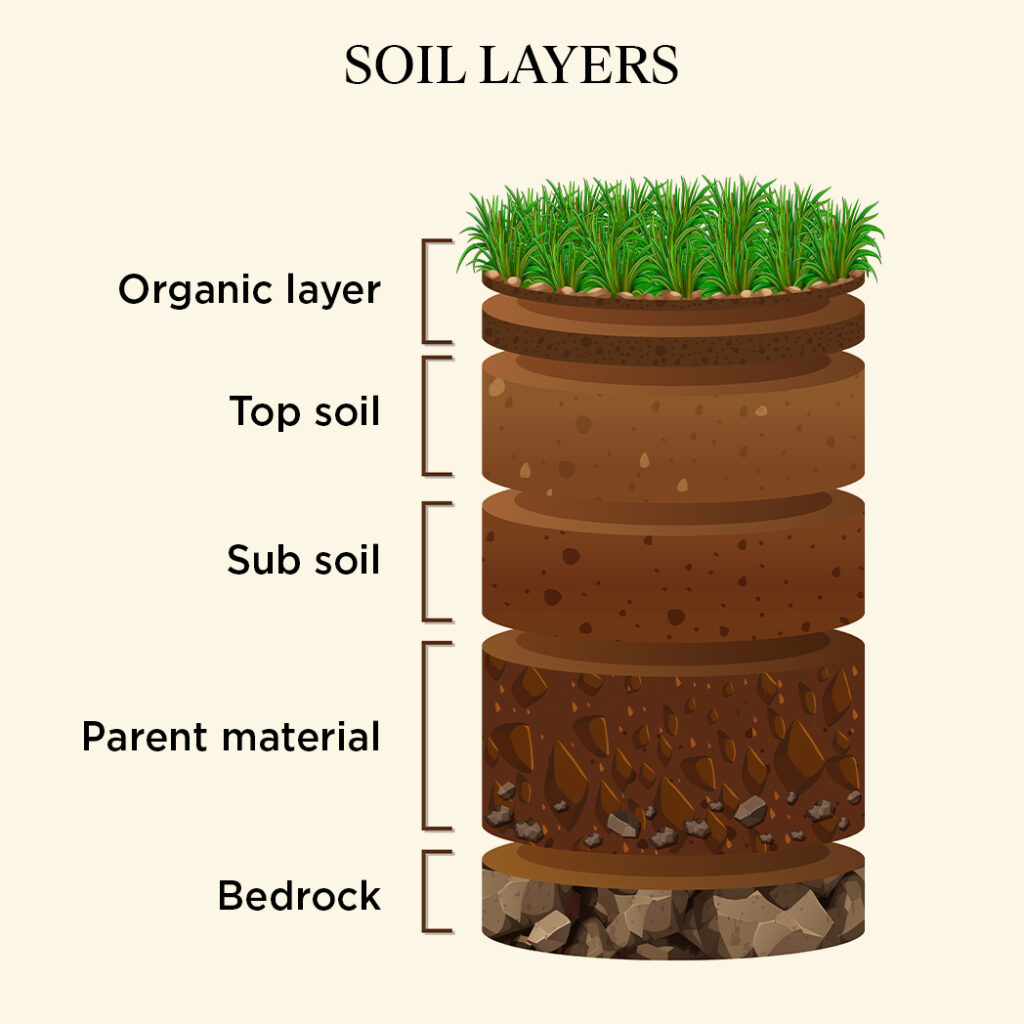
Purpose of Soil
Purpose of Soil is to provide plants a firm grip to stand stall and supply essential nutrients for plant growth. Now you can clearly see how soil takes role of mother for plants too.
In soil all 3 states of matter are present – Solid, Liquid and Gas. In ideal situation the soil has
Solid Phase(Mineral Matter)
Mix of organic and inorganic matter together form bulk of soil state- carbonate, silicate and various salt , iron, aluminium oxide etc.
Liquid Phase(Soil Water)
Between the small particle of soil there are gaps or pores about 40-50% volume of soil is occupied by soil pores. Partially or fully filled with water, when we water a plant pot air trapped in the spore comes out in the form of bubbles. Water trapped in the pore has dissolved salt in it which provides nutrition to the plant. Nutritious water trapped in the soil works as reservoir for water supply.
Gaseous Phase(Soil Air)
Part of the pores which is not filled with water is called gaseous phase of the soil system. In the Like any half-filled glass or water bottle remaining area is captured with air/gas. So the a volume of the air is thus dependent on that of water. Interestingly, air has nitrogen (N2),oxygen (O2) and carbon (CO2) in it but air in pores has much higher soil CO2 concentration that our regular atmospheric air while Nitrogen and oxygen percentage remains same.
Textures of Soil

Soil is made up of three key constituents namely Sand, Clay and Silt.
Clay– Smallest particle in soil measuring less than .002 mm in diameter, It is the mostly found soil particles in the earth crust available for gardening purpose. They can retain good amount of water and most compact compared to sand and silt. Since they are good at retaining water, they provide maximum nutrients to plants for growth.
Sand– The sand particles are biggest particles, which ranges between 0.2 to 2 mm in diameter classified as coarse sand and relatively smaller sand particle 0.02 to 0.2 mm in diameter referred as fine sand. Think of Soil particles as hundreds of balls kept in big jar, as we increase the size of the balls empty space left between balls (pore) increases proportionally. If there is empty space it will allow air or water to flower easily. Because of the larger size sand allows faster passage of air and water in garden soil. However the sand contains less mineral as compared to silt and clay, so high percentage of sand will make your mix drain faster, free flow of air/less compaction but won’t offer much in nutrition as it has less minerals.
Silt-Size of silt particles is between 0.02 to 0.002 mm in diameter. The silt particles because of their size can hold more water than sand particles and is more compact. Silt contain medium quantity of the mineral, offer more nutrition to plants than sand. Hence is desired material for gardening.
This brings us to the topic what are the factor that affect our gardening success.
Well like our wellbeing there are millions of factor that contribute to happy plant. One more reason for us to believe they are just like us! But good news is for acing our gardening game we just need to take care of only few things.
PH of Soil
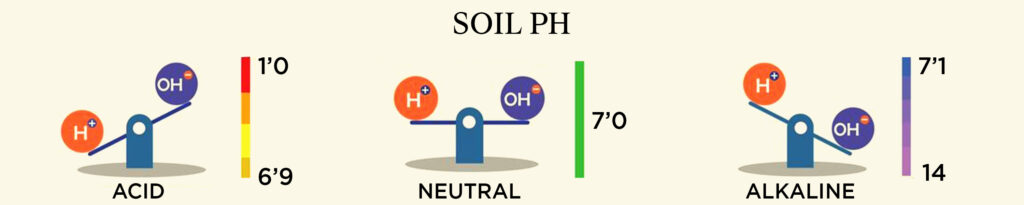
Ph: We have understood the physical properties of the soil now let’s understand on chemical properties.
From Science definition: “pH is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion activity. The pH of a soil indicates its acidity or alkalinity. If that sounds too nerdy, pH determines if the soil is acidic or alkaline. pH scale works on 0-14 range, a reading below 7 refers to acidic soil and above is alkaline soil.
But more importantly why should we know about pH level? pH of soil determines availability of nutrients to plant.
Now we learnt that nutrients (N,P,K etc.) are dissolved in water trapped in the pore of soil and plant consumes these dissolved nutrient for growth. But if the soil is too alkaline or acidic, nutrients will not get dissolved. Availability of different nutrient varies with change in pH, a 6.0 – 7.5 pH range is optimum for almost all nutrients are available (dissolved in water).
From home gardening point of view pH 6.5 just perfect pH level of most of the house plants.
How to check pH of a soil?
If you are getting soil from trusted brands online/offline then it will be already in the right pH range. However if you are using common available soil from lawn or local area to check you can use of a pH meter from a authentic source or using a pH testing kit.
There are other hacks to get a sense if your soil is acidic or alkaline, if you observe the deposition of salt or white substance on the upper surface of the soil indicates soil is alkaline.
Take spoonful sample of soil in cup and add ½ cup vinegar, If the mixture forms bubbles or frizzles out, your soil is alkaline.
Take spoonful sample of soil in a glass and mix it with distilled water. Add ½ cup baking soda. If solution forms bubbles, you have acidic soil.

Organic Matter : Living Soil
- Organic matter also supplies hormones (Auxin ,Gibberellins , IAA), antibiotics and supplies essential nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulphur for plant growth.
- pH Control: During decomposition released organic acids helps in maintaining pH while CO2 released aids in plant food preparation.
- Aeration: Improves aeration and water holding capacity of by forming granular structures.
- Provides temperature control during summer and winters.
Clear indicator of organic matter and biological activity in soil is “Petrichor”, The scent released during light rain, is primarily due to release of trapped gas in pores of soil. These pleasant smell is due a compound (geosmin) produced by bacteria in soil. This has led some researchers to suggest that humans have a natural affinity for this scent due to its potential role in our ancestors’ survival. Interestingly, camels rely on petrichor to locate sources of water in the desert.
FACT-Earthworms are often referred as Soil Engineer, so next time when you see a earthworm calling out of you garden or pot don’t freak out. It just says that soil is very much active and alive, a good news indeed.
TYPES OF SOIL IN INDIA (Small table with infographic only )
FUN FACT
In nature Soil is available in many colours red, brown, black, yellow, and even blue. These colours governed by the minerals and organic matter present in soil.
It can take up to 1,000 years to form just one inch of topsoil, making it a valuable and non-renewable resource.
A teaspoon of soil can contain billions of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and earthworms.
Add table
- type of soil in India
- Ph image for nutrient availability
- pH requirements of crops
4, Add a chapter section on EC fromSuji
5 removed ph – create new chapter
6 removed soil amendments – create new chapter or potting mix




